CHRS Data Portal
Global satellite precipitation data archive from UC Irvine's CHRS. Access PERSIANN system data (1983-present) with visualization and download tools for spatiotemporal precipitation statistics.
A curated collection of open-source tools, code libraries, and foundational datasets for landslide research to promote academic exchange and collaboration.
Global satellite precipitation data archive from UC Irvine's CHRS. Access PERSIANN system data (1983-present) with visualization and download tools for spatiotemporal precipitation statistics.
A Python tool for landslide susceptibility mapping and uncertainty analysis.
Landslide Hazard Assessment for Situational Awareness (LHASA) Model - A NASA-developed system for near real-time landslide hazard assessment.
A QGIS framework for physically-based probabilistic modelling of landslide susceptibility.
Free open-source geospatial modeling tool for hydro-meteorological surface hazards. Features scripting environment, data viewer, and Python bindings for automation and integration.
LiCSBAS is an open-source package in Python and bash to carry out InSAR time series analysis using LiCSAR products (i.e., unwrapped interferograms and coherence) which are freely available on the COMET-LiCS web portal. LiCSBAS2 is the successor of LiCSBAS. Users can easily derive the time series and velocity of the displacement if sufficient LiCSAR products are available in the area of interest. LiCSBAS also contains visualization tools to interactively display the time series of displacement to help investigation and interpretation of the results.
Landslide mapping system from NASA. Uses object-based image analysis (OBIA) and a Random Forest classifier on optical imagery and a digital elevation model (DEM). Requires training polygons and runs in a Singularity container on Linux.
TerraTrack is an open-source, cloud-based workflow for detecting and monitoring slow-moving landslides using Sentinel-2 imagery and optical feature tracking. For further details, please consult the paper "A Workflow to Identify and Monitor Slow-Moving Landslides through Spaceborne Optical Feature Tracking" by Nava et al (2025).
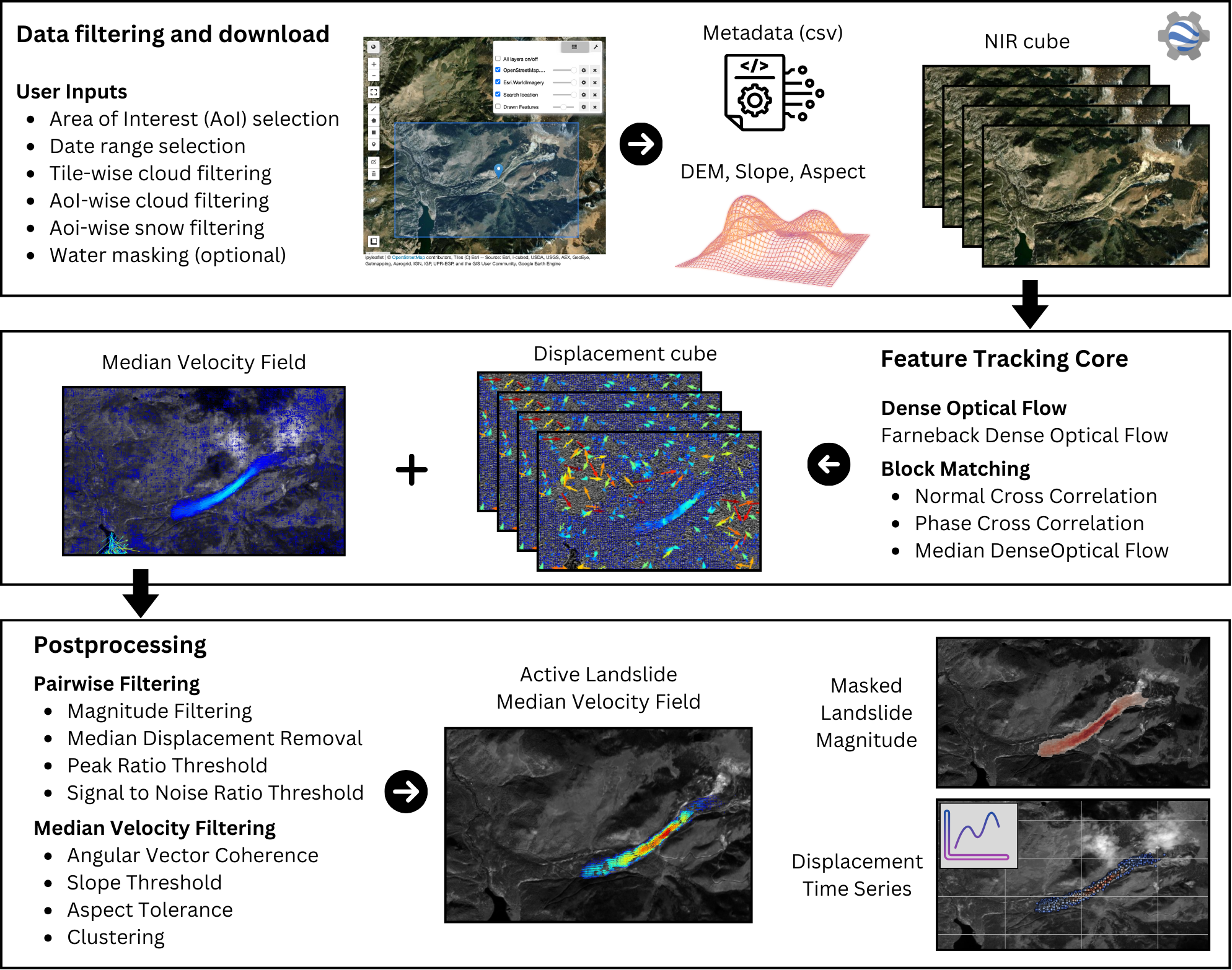
Scripts performing k-means segmentation and merging to extract candidate objects from optical imagery, followed by Random Forest classification. Built on Google Earth Engine and Python libraries; replicates a 2019 MSc thesis. Associated publication: Thesis: Landslide Detection using Random Forest Classifier (TU Delft, 2019)
Python/GEE script for rapid landslide mapping using Sentinel-2. Calculates the Barren Soil Index (BSI), NDWI, and NDVI to highlight barren soil, water, and vegetation, then classifies landslides based on thresholds.
Code and sample data enabling training of an Attention U-Net segmentation model on Sentinel-1 SAR amplitude data. Based on data from the 2018 Hokkaido event. Associated publication: Rapid Mapping of Landslides on SAR Data by Attention U-Net (Remote Sensing 2022)
Repository with code and sample data for the HR-GLDD dataset. Enables training segmentation models using generalized DL for rapid landslide mapping on high-resolution satellite imagery. Associated publication: HR-GLDD: A globally distributed dataset using generalized DL for rapid landslide mapping on high-resolution satellite imagery (Remote Sensing 2022)
This repository presents an all-weather, day-night SAR-based Co-Seismic Landslide Rapid Assessment tool (SAR-LRA). Using deep neural networks, the tool is designed to detect landslides during earthquake-triggered, multi-landslide events.
Deprecated demonstration package from NASA for automated Landsat-based landslide detection in Nepal. Combines Landsat imagery with rainfall monitoring; depends on GDAL, SciPy etc. Associated publication: Automated Satellite-based Landslide Identification Product for Nepal (Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2018)
BRIGHT is the first open-access, globally distributed, event-diverse multimodal dataset that integrates very-high-resolution optical and SAR imagery, enabling truly all-weather, day-and-night building damage assessment. It fills a major gap in high-quality benchmarks by providing 0.3–1 m building-level imagery across 14 regions and seven disaster types, supporting the development of robust AI models for real-world disaster response. The dataset also includes standardized baselines from advanced AI models, offering a consistent foundation for research on transferability, domain adaptation, semi-supervised learning, and multimodal change detection.
A comprehensive database of landslide damages and losses across the United States, providing critical information for risk assessment, mitigation strategies, and understanding the economic and social impacts of landslide hazards.
The GlobalBuildingAtlas (GBA) is a new, free, public dataset that provides the first complete 3D map of nearly every building on Earth. It contains over 2.75 billion building polygons, exceeding previous databases by more than 1 billion instances. The height data have a spatial resolution of 3 m × 3 m, which is 30× finer than the previous global standard of 90 m. The dataset includes 2.68 billion 3D building models, achieving a height completeness rate of over 97%. Model accuracy is evaluated using Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), ranging from 1.5 to 8.9 m across different continents.
913 flood maps, along with .csv files containing population exposure metrics for each event, are available for viewing and download on Cloud to Street's website and in the Google Earth Engine Catalog. Code to reproduce the MODIS algorithm or the entire database, data for each country, and all underlying data and scripts used to create the figures in the paper are available in the GitHub repository.
OpenLandMap-soildb delivers global, time-resolved soil predictions at 30 m resolution for 2000-2022+ using spatiotemporal machine learning and harmonized legacy soil observations. It maps key soil properties (e.g., SOC content/density, pH, texture, bulk density) and USDA soil subgroup probabilities with per-pixel uncertainty, enabling high-resolution analysis of soil condition and change.
GeoElastix, a state-of-the-art remote sensing registration library designed to address the complex challenges of georectification for geospatial datasets.
Why it matters:
✅ Flexible & intelligent — Choose from multiple registration methods tailored to your data's unique challenges
✅ Built for Scale: Seamlessly handles nodata areas, automatic tiling for large datasets, batch processing to save you hours of manual work, and generates comprehensive report outputs
✅ Modern open-source design — Clean architecture, thorough documentation, and a community-driven approach.
🌍 Your go-to channel for mastering open-source geospatial analysis, visualization, and cloud computing.
Here, you'll learn how to use powerful tools such as Earth Engine, Geemap, Leafmap, GeoAI, and other Python GIS libraries to analyze and visualize geospatial data at scale. Whether you're a researcher, developer, or GIS professional, this channel provides practical tutorials, demos, and workflows to help you level up your skills in GeoAI, remote sensing, and geospatial programming.
📌 What you'll find here:
✅ Step-by-step Earth Engine tutorials using Python
✅ Hands-on guides for geemap, leafmap, and MapLibre
✅ GeoAI and machine learning workflows for remote sensing
✅ Tips for cloud-native geospatial computing
✅ Best practices for GIS programming and open-source tools
3Blue1Brown is Grant Sanderson's YouTube channel that explains difficult math topics through clear, animation-driven storytelling. It covers linear algebra, calculus, neural networks, and more, with an emphasis on intuition and conceptual understanding.
GRASS GIS based multiphase mass-flow simulator for cascading landslide, debris-flow, and GLOF scenarios.
USGS-oriented dense granular-fluid flow solver built on Clawpack for debris flows and landslide-tsunami cascades.
GPU-first dynamic simulator for flood, landslide, and debris-flow processes with modern workflow integration.
Julia ecosystem for high-performance MPM simulation targeting extreme large-deformation landslide dynamics.
Backend-agnostic high-performance MPM solver from the LandslideSIM stack.
Structured material-point generation toolkit for preparing MPM input geometry from terrain point data.
Julia visualization companion for exporting MPM simulation outputs for 3D inspection and ParaView workflows.
Open-source Anura3D implementation for large deformation and soil-water-structure interaction modeling.
Lightweight Python runout/intensity estimator for gravitational mass flows using efficient geometric routing.
Mass-flow simulation software widely used for debris-flow hazard analysis and scenario planning.
iRIC ecosystem including Kanako and DFSS solvers for mountain-channel debris-flow and sabo engineering analyses.
Kanako is an open debris-flow simulator in the iRIC ecosystem for mountain channel and sabo studies.
DFSS extends iRIC workflows for debris-flow and sabo-oriented numerical experiments.
GPU-native SPH simulation engine supporting advanced incompressible formulations and spatial adaptivity.
Educational 2D SPH implementation suitable for understanding weakly compressible formulations.
3D slope-stability plugin with ellipsoidal slip-surface sampling, FoS mapping, and optional groundwater assumptions.
Constrained random-walk routing model for probabilistic runout and impact indicator mapping.
GRASS add-on implementation related to random-walk style mass-movement routing analysis.
Automated slope-unit delineation and cleaning toolkit for geomorphologically meaningful mapping units.
Rock-slope kinematic stability and SMR assessment module for planar, wedge, and toppling failure modes.
GRASS add-ons for runout and deposition modeling, including modernized C-based and parallelized implementations.
Frequency-ratio based susceptibility mapping tool with built-in k-fold validation workflow.
R-based susceptibility ensemble framework combining multiple statistical classifiers with uncertainty estimation.
LAND-SE companion suite for data preparation, variable screening, and statistically based zonation workflows.
Modular project manager for susceptibility studies, supporting AHP, WoE, classifier runs, and map outputs.
QGIS plugin for susceptibility mapping with GAM and machine learning methods on raster or vector units.
Fast Shallow Landslide Assessment Model plugin focused on rainfall-induced shallow landslide susceptibility.
MATLAB toolbox for rapid landslide susceptibility mapping with multiple machine learning models.
GRASS GIS add-on for ANN-based landslide susceptibility mapping with environmental predictor layers.
Python system for regional susceptibility assessment and classifier benchmarking in loess and similar terrains.
Free geospatial analysis platform with fuzzy inference capabilities for susceptibility-oriented workflows.
CAPRA landslide toolbox for simplified physically based safety-factor calculations and scenario screening.
UNet++ style implementation for optical plus near-infrared landslide segmentation.
Multi-scale feature fusion framework for landslide detection across mixed satellite and UAV imagery.
Curated benchmark dataset designed for training and evaluating deep learning landslide detection models.
Multi-source optical plus DEM based deep learning workflow for landslide mapping across regions.
SAR datacube deep learning implementation for rapid post-event landslide mapping in cloudy conditions.
Global rainfall-induced landslide risk modeling codebase using statistical and ML components.
Workflow code to evaluate SAR effectiveness for mapping landslide-related surface damage.
Google Earth Engine landslide susceptibility mapping scripts for large-scale cloud workflows.
Open-source InSAR time-series processing package built around LiCSAR products and displacement analysis.
Large-scale wireless sensor network program for landslide monitoring and dynamic warning decisions.
Open hardware and software stack for low-cost slope displacement monitoring with satellite backhaul.
Prototype IoT early-warning code integrating vibration and tilt sensing with local ML inference.
Deep learning based embedded pipeline for low-cost landslide monitoring and warning prototypes.
Open-source implementation for susceptibility mapping using machine learning and CNN-based methods.
Large-scale multisensor landslide benchmark dataset for deep-learning based detection research.
Global susceptibility raster used by LHASA workflows as a baseline conditioning layer.
Practical Medium walkthrough for event-focused landslide mapping in Google Earth Engine.
Video tutorial for Sentinel-1 SAR based landslide mapping and thresholding workflows in Earth Engine.
Step-by-step Sentinel-2 based landslide detection tutorial in the Earth Engine code editor.
Official geemap tutorial library for notebook-based Earth Engine workflows and mapping.
Introductory tutorial focused on downloading and organizing global landslide inventory inputs.
Companion practical tutorial for preparing cleaned landslide inventory maps in common GIS tools.
Colab-centered workflow pattern for multicollinearity checks and machine-learning susceptibility mapping.
Example notebook-style workflow for SAR-based landslide analysis using cloud notebook tooling.
Open workshop materials for spatiotemporal climate and satellite image processing in Python.
Workshop repository with reproducible material for geoscience modeling workflows in Python.
Public competition notebook demonstrating model experimentation for landslide-focused workflows.
Indexed notebook links and references useful for reproducing landslide detection competition pipelines.
End-to-end notebook example for landslide detection experiments and evaluation on open data.
Curated list of open geoscience tools, data resources, and learning references.
Official tutorials covering input preparation, weight range analysis, sensitivity, and map generation.
Global 30 m Copernicus digital elevation model derived from TanDEM-X and distributed through multiple open platforms.
Shuttle Radar Topography Mission elevation baseline used for global landslide terrain derivatives and long-running regional workflows.
ASTER Global DEM Version 3 from LP DAAC, commonly used as an alternative global terrain source in susceptibility and hazard studies.
Global lithological map database used to encode rock-type controls on slope stability and material properties at planetary scale.
Global active-fault compilation for tectonic conditioning and distance-to-fault predictors in geohazard assessment.
Global near-surface shear-wave velocity mosaic (Vs30) for geotechnical and site-condition context in hazard modeling.
NASA IMERG multi-satellite precipitation product with 30-minute temporal resolution for rainfall-triggered landslide analysis.
CHRS PERSIANN precipitation family including near-real-time PDIR-Now and climate-scale CDR products for triggering analysis.
NASA SMAP soil-moisture products and companion open notebooks for antecedent wetness and hydrologic state characterization.
Copernicus operational soil-moisture suite providing surface soil moisture and Soil Water Index layers for hydrogeologic monitoring.
USGS authoritative earthquake catalog used to derive seismic triggering indicators and event-based landslide context.
Global 10 m land-cover map from ESA, widely used for environmental conditioning factors in landslide susceptibility studies.
Near-real-time 10 m global land-cover predictions for rapidly updated surface-condition context.
Long-term 30 m global land-cover dynamics product for historical change analysis in susceptibility and risk workflows.
Global 10 m land-cover dataset with a fine classification system built from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 time-series data in Google Earth Engine.
Harmonized Landsat Sentinel-2 vegetation index products (including NDVI/EVI/NBR family) for high-frequency vegetation condition tracking.
Harmonized global road-network dataset useful for exposure, accessibility, and anthropogenic conditioning analysis.
Event-level global landslide inventory used for benchmarking and hazard model validation, especially rainfall-triggered landslides.
Classic physically based shallow-landslide model coupling infinite-slope stability with topography-controlled steady-state hydrology; includes GRASS GIS implementation.
Stability Index Mapping model using steady-state hydrology plus parameter-range uncertainty to produce probability-oriented slope-stability zoning.
USGS transient rainfall infiltration and grid-based slope-stability model for rainfall-triggered shallow landslide forecasting.
Physically based hydrologic-geotechnical framework coupling GEOtop water-energy processes with slope-failure assessment for shallow landslides and debris-flow initiation.
High-resolution physically based slope-stability simulator designed for parallel and HPC environments with probabilistic uncertainty treatment.
Combined Hydrology And Slope Stability Model for transient infiltration and slope-stability assessment, with web-based early-warning deployment options.
USGS 3D slope-stability software that searches large numbers of rotational failure surfaces across digital landscapes using 3D limit equilibrium.
Research-stage 3D translational shallow-landslide model focusing on DEM-cell side resistance and improved treatment of discretization effects.
Integrated physically based simulator for debris-flow initiation and runout with dual triggering mechanisms and entrainment-deposition dynamics.
Integrated rapid-landslide model for earthquake and rainfall triggering, progressive failure, and long-runout motion analysis.
Physical assessment framework designed to integrate shallow and deep landslide mechanisms within a unified susceptibility and hazard workflow.
Python-based Earth-surface modeling framework with a landslide component for physically based probability analysis and multi-process coupling experiments.
Legacy Level I Stability Analysis framework that introduced probabilistic slope-stability screening concepts for large-area planning applications.
Open catastrophe risk framework with standardized exposure pipelines for multi-hazard loss workflows.
Industry-standard open schema for exposure records used to exchange asset, location, occupancy, and financial terms across risk models.
OpenQuake exposure-model specification and ingestion workflows for structured asset-level risk calculations.
GEM exposure database initiative covering asset classes and taxonomy structures for multi-hazard global risk analysis.
Open climate-risk framework with exposure construction and adaptation-oriented impact assessment workflows.
Open QGIS-based scenario workflow to intersect hazards with exposure layers and estimate affected population and assets.
Open risk decision-support framework for tracking and evaluating changes in exposure and losses across time and scenarios.
Open framework for harmonizing multi-sector data to evaluate cross-sector exposure and cascading impacts.
IWMI flood-risk mapping workflow integrating hazard frequency with socioeconomic exposure layers.
Open repositories from FEMA NHRAP supporting exposure and loss-processing workflows aligned with Hazus methods.
Copernicus GHSL spatiotemporal settlement products providing built-up surface, volume, and population-linked exposure layers.
Global AI-derived building footprint polygons with broad geographic coverage for asset exposure baselining.
Temporal building-exposure dataset from Google Research with building presence and change metrics for repeated monitoring.
Global three-dimensional building footprint product with estimated building heights for volumetric exposure analyses.
OSM-driven building exposure project focusing on harmonized footprints and semantic enrichment for risk modeling pipelines.
Open gridded population products with demographic variants used for high-resolution exposure and humanitarian planning.
Settlement-informed high-resolution population exposure layers derived from building detection and census redistribution.
Global ambient population distribution product representing diurnal exposure patterns for emergency and risk analyses.
Gridded Population of the World version 4.11, providing globally consistent census-based population exposure surfaces.
Have you developed an excellent landslide research tool? Share it with the community to help drive collective progress in the field.
Submit New Tool